Blog
LSD vs. Psilocybin
LSD vs. Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms): A Comparative Exploration
Psychedelic substances have long fascinated researchers, users, and cultural movements. Two of the most well-known psychedelics are LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) and psilocybin, the active compound found in magic mushrooms. While both substances can produce similar effects, such as altered states of consciousness, mystical experiences, and changes in perception, they differ significantly in their chemical composition, effects, mechanisms of action, history, and cultural significance. This article explores the differences and similarities between LSD and psilocybin to provide a comprehensive understanding of these two powerful substances. LSD vs. Psilocybin
Introduction to Psychedelics
Psychedelics are substances that alter perception, mood, and various cognitive processes. LSD and psilocybin are both classified as serotonergic psychedelics, meaning they primarily affect serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to their profound psychoactive effects. Despite their similarities, these substances have distinct qualities that shape the user experience and their potential therapeutic applications. LSD vs. Psilocybin
What is LSD?: LSD vs. Psilocybin.
Chemical Composition and Synthesis
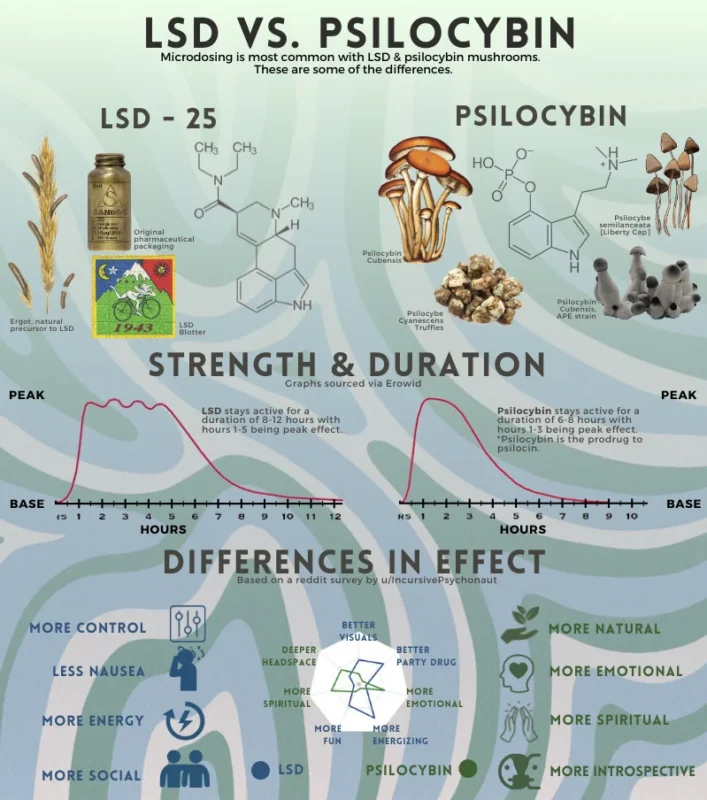
LSD is a synthetic compound that was first synthesized in 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann at the Sandoz Laboratories. It is derived from ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and other cereals. The substance is typically administered as small tablets, capsules, or liquid, and its potency is often measured in micrograms due to its extremely small effective dose. LSD vs. Psilocybin
How LSD Works
LSD primarily interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor, leading to alterations in mood, cognition, and perception. It also influences dopamine and glutamate systems, contributing to the compound’s stimulating and hallucinogenic effects. The effects of LSD are often characterized by vivid hallucinations, time dilation, enhanced sensory perception, and profound emotional experiences. LSD vs. Psilocybin
The Effects of LSD
LSD’s effects are typically felt within 30 to 90 minutes after ingestion, lasting anywhere from 8 to 12 hours. The experience can vary significantly depending on the dose, the environment, and the individual’s mindset, often referred to as “set and setting.” Some common effects include:
- Visual Hallucinations: Colors may appear more vivid, patterns may shift, and objects might appear to breathe or distort.
- Altered Perception of Time: Time can seem to slow down or speed up.
- Euphoria and Insights: Users may experience heightened emotions, feelings of interconnectedness, and insights into their own psyche or the nature of existence.
- Negative Effects: Anxiety, paranoia, and confusion can occur, especially in unfamiliar or uncomfortable environments.
What is Psilocybin?
Chemical Composition and Natural Source
Psilocybin is a naturally occurring compound found in certain species of mushrooms, often referred to as “magic mushrooms.” It is chemically classified as a tryptamine, closely related to serotonin. Psilocybin is converted into psilocin in the body, which then produces the psychedelic effects. The use of psilocybin mushrooms dates back thousands of years, with indigenous peoples in Central and South America using them in religious and spiritual rituals. LSD vs. Psilocybin
How Psilocybin Works
Like LSD, psilocybin primarily affects serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. However, psilocybin’s effects are generally considered to be less intense and more grounded compared to LSD. Psilocybin also has a less pronounced effect on dopamine systems compared to LSD, which may explain why the experiences are often perceived as more introspective and less stimulating. LSD vs. Psilocybin
The Effects of Psilocybin
The effects of psilocybin typically begin within 20 to 40 minutes of ingestion and last for about 4 to 6 hours. While both substances can induce intense perceptual changes, psilocybin is often considered a more “natural” and “earthy” experience. Common effects of psilocybin include:
- Visual Distortions and Hallucinations: Similar to LSD, colors may become more vibrant, and users may see geometric patterns or trails of light.
- Introspection: Psilocybin often leads to deep introspection, with users reflecting on their personal life, relationships, and even existential concepts.
- Emotional Shifts: Many users report feeling a deep sense of connection to nature, the universe, or other people.
- Potential for “Bad Trips“: As with LSD, negative experiences such as anxiety, paranoia, and fear are possible, although they tend to be less frequent with psilocybin.
Key Differences Between LSD and Psilocybin
1. Chemical Structure and Origin
One of the most significant differences between LSD and psilocybin is their origin and chemical structure. LSD is a synthetic substance, meaning it is artificially created in a laboratory, while psilocybin occurs naturally in certain mushrooms. This difference may influence the subjective experiences of users, as natural substances are often perceived as more grounded and connected to nature. LSD vs. Psilocybin
2. Duration of Effects
The duration of effects is one of the most striking differences between LSD and psilocybin. LSD tends to have a much longer duration, with effects lasting anywhere from 8 to 12 hours. In contrast, psilocybin’s effects are typically shorter, lasting between 4 to 6 hours. This longer duration can make an LSD trip feel more intense and overwhelming, especially for inexperienced users. LSD vs. Psilocybin
3. Intensity of Experience
LSD is often described as more intense and stimulating compared to psilocybin. While both substances can induce powerful visual and auditory hallucinations, LSD is typically associated with a more fast-paced and energetic trip. In contrast, psilocybin trips tend to be more introspective and grounding, with users reporting a greater sense of emotional and spiritual insight. LSD vs. Psilocybin
4. Psychological Effects
Both LSD and psilocybin can induce significant shifts in perception and consciousness, but the nature of these shifts can differ. LSD is often associated with ego dissolution, where users feel as though their sense of self breaks down, leading to a profound sense of interconnectedness with the universe. Psilocybin also has the potential for ego dissolution, but the experience is often more gentle and introspective. LSD vs. Psilocybin
5. Visual and Auditory Hallucinations
LSD is known for its powerful visual hallucinations, which can be intense and fast-moving. Users may see complex geometric patterns, vivid colors, and surreal imagery. Psilocybin also induces visual hallucinations, but they tend to be less complex and more organic, with users often seeing nature-inspired visuals, such as flowers or fractal patterns. LSD vs. Psilocybin
6. Risk and Safety
Both substances are considered to have a low potential for physical harm or toxicity. However, the psychological effects of both LSD and psilocybin can lead to challenging experiences, especially in individuals who are predisposed to mental health conditions like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Both substances can cause “bad trips,” which are marked by intense fear, anxiety, and paranoia, but psilocybin is often seen as gentler in this regard. LSD vs. Psilocybin
Similarities Between LSD and Psilocybin
1. Serotonergic Activity
Both LSD and psilocybin primarily exert their effects through serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor. This is why their experiences are often described as similar, with both substances leading to altered states of consciousness, visual distortions, and intense emotional experiences. LSD vs. Psilocybin
2. Therapeutic Potential
Both substances have been explored for their potential therapeutic benefits, particularly in the treatment of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Research has shown that psilocybin may promote neurogenesis (the growth of new brain cells) and has been used in clinical trials to treat end-of-life anxiety in terminal cancer patients. LSD, too, has been studied for its potential in treating depression, alcoholism, and anxiety, with promising results emerging from modern studies. LSD vs. Psilocybin
3. Spiritual and Mystical Experiences
Both LSD and psilocybin are known to induce profound spiritual or mystical experiences. Users often report feelings of oneness with the universe, a sense of timelessness, and an enhanced sense of meaning in life. These experiences have contributed to the use of both substances in religious and therapeutic settings. LSD vs. Psilocybin
4. Popularity in the Counterculture
Both LSD and psilocybin gained significant popularity during the 1960s, becoming central to the counterculture movement. Figures like Timothy Leary championed the use of psychedelics for expanding consciousness, and psilocybin mushrooms were particularly prominent in indigenous spiritual practices. LSD vs. Psilocybin
Conclusion
In conclusion, while LSD and psilocybin share many similarities as serotonergic psychedelics, they differ significantly in their chemical structure, duration of effects, and intensity of experience. LSD tends to be more intense, long-lasting, and stimulating, while psilocybin is often considered more grounded, introspective, and organic. Both substances have demonstrated therapeutic potential, and their cultural significance continues to grow as research on psychedelics expands. Whether one prefers the synthetic, high-energy trip of LSD or the natural, introspective journey of psilocybin largely depends on personal preferences and the specific goals of the user. LSD vs. Psilocybin