Blog
MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
MDMA in Mental Health Treatment: Exploring the Therapeutic Potential
MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), commonly known as ecstasy or molly, is a psychoactive drug that has gained increasing attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic applications, especially in the treatment of mental health conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety. Initially popularized as a recreational drug, MDMA has sparked interest within the medical community due to its unique effects on the brain, particularly in enhancing emotional processing, increasing empathy, and improving social interactions. In this article, we will explore the scientific basis for MDMA’s use in mental health treatment, its benefits, risks, and the ongoing research that is shaping its potential role in modern therapy. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
1. Introduction to MDMA and Its Effects: MDMA in Mental Health Treatment.
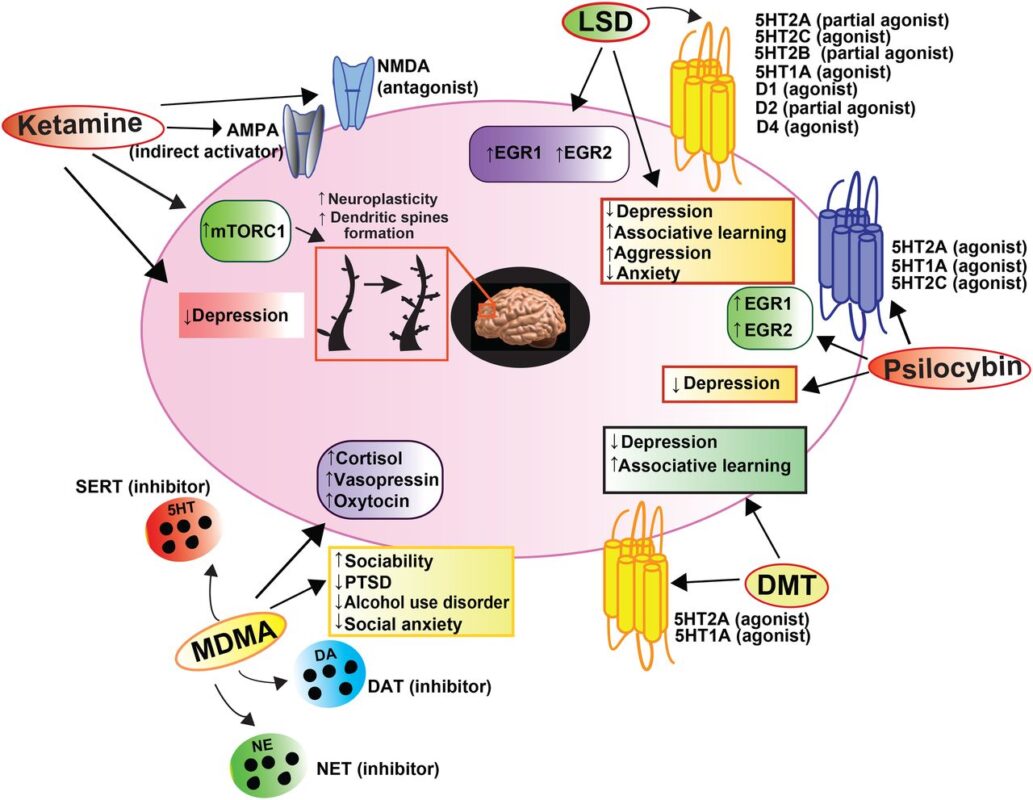
MDMA is a synthetic compound that primarily affects the brain’s serotonin system. It has stimulant and empathogenic (empathy-producing) properties, which often result in feelings of euphoria, emotional openness, and a heightened sense of connection to others. These effects make MDMA an attractive candidate for therapeutic use in conditions where emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships are central issues, such as PTSD. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
1.1 The Mechanism of Action
MDMA’s psychoactive effects are largely attributed to its action on serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. By increasing the release of serotonin, MDMA promotes feelings of emotional closeness and well-being. Serotonin plays a key role in mood regulation, and its increased release during MDMA use can help individuals confront difficult emotions, which is especially beneficial in therapeutic settings for those with trauma-related disorders.
In addition to its serotonergic effects, MDMA also increases dopamine and norepinephrine levels, which contribute to heightened energy, focus, and feelings of pleasure. This combination of effects has led researchers to explore how MDMA could aid in psychotherapy by helping patients access and process difficult emotional material.
1.2 Overview of MDMA’s Therapeutic Applications
While MDMA is known for its recreational use, it is being increasingly studied for its potential benefits in treating a variety of mental health conditions, including PTSD, depression, anxiety, and social anxiety. The drug’s ability to enhance emotional experiences and promote a sense of connection with others makes it particularly useful in therapies that focus on emotional healing and interpersonal relationships.
2. MDMA-Assisted Psychotherapy for PTSD
One of the most promising applications of MDMA in mental health treatment is its use in the treatment of PTSD. PTSD is a condition that often results from experiencing or witnessing traumatic events, such as violence, natural disasters, or military combat. Symptoms of PTSD can include flashbacks, nightmares, emotional numbness, and difficulty trusting others. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
2.1 Mechanisms of MDMA in PTSD Treatment
MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD has gained significant attention in recent years, with studies showing that the drug can help patients access and process traumatic memories in a way that is not as overwhelming as traditional therapeutic methods. The emotional openness induced by MDMA allows patients to confront difficult memories and emotions, which might otherwise be too painful to face.
MDMA’s ability to reduce fear responses and promote a sense of safety is a key factor in its therapeutic effects. Patients who undergo MDMA-assisted therapy report feeling more emotionally connected to their therapists, as well as more empathetic and less defensive. This can create a therapeutic alliance that is critical for healing trauma.
2.2 Research and Clinical Trials
Research into MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD began in the early 2000s, and since then, several clinical trials have been conducted to explore its efficacy. One of the most notable studies, conducted by the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), demonstrated significant improvements in PTSD symptoms after a series of MDMA-assisted therapy sessions. In the study, patients who underwent MDMA-assisted psychotherapy showed a substantial reduction in PTSD symptoms, with many experiencing remission after treatment.
The results of these trials have been groundbreaking, and they have led to a growing interest in using MDMA as a treatment for PTSD. The success of these trials has prompted the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to designate MDMA-assisted psychotherapy as a “breakthrough therapy” for PTSD, which could accelerate its development for wider clinical use.
2.3 Advantages of MDMA in PTSD Treatment
MDMA’s potential advantages in treating PTSD include its ability to reduce anxiety and fear, which are often barriers to traditional therapeutic methods. For individuals with PTSD, confronting traumatic memories can be difficult and emotionally distressing. MDMA can make this process more manageable by allowing patients to experience these memories in a less overwhelming manner.
Additionally, the enhanced feelings of empathy and trust that MDMA induces can strengthen the patient-therapist relationship, providing a supportive and safe environment for emotional exploration. This, in turn, facilitates the therapeutic process and promotes healing. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
3. MDMA in Treating Anxiety and Depression
In addition to PTSD, MDMA is also being investigated for its potential to treat mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Individuals with these conditions often struggle with feelings of hopelessness, isolation, and emotional numbness, which can make it difficult to engage in therapy and develop meaningful connections with others. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
3.1 Mechanisms of MDMA in Treating Anxiety and Depression
MDMA’s effects on serotonin levels are thought to play a significant role in its potential to treat anxiety and depression. By increasing serotonin release, MDMA can help improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety. The drug’s empathogenic effects also allow patients to feel more connected to others, which can help alleviate feelings of isolation and emotional numbness. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
Additionally, MDMA’s ability to enhance emotional processing and facilitate the expression of difficult emotions may allow patients with depression and anxiety to gain new insights into the underlying causes of their conditions. This can provide a foundation for more effective therapeutic interventions. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
3.2 Research on MDMA for Anxiety and Depression
Although most research on MDMA-assisted psychotherapy has focused on PTSD, studies have also shown promise in treating other mental health conditions. For example, a study published in the journal Psychopharmacology explored the use of MDMA in patients with social anxiety, particularly in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study found that MDMA significantly reduced social anxiety and improved participants’ ability to interact socially. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
Other research has suggested that MDMA could be beneficial for individuals with treatment-resistant depression, particularly when combined with psychotherapy. The emotional openness induced by MDMA may help patients explore their depression in a way that traditional medications have not been able to achieve. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
4. The Role of MDMA in Enhancing Therapeutic Processes
One of the primary reasons MDMA has been studied in therapy is its ability to facilitate deep emotional exploration. In traditional psychotherapy, patients may have difficulty confronting difficult emotions or trauma due to fear or emotional blockages. MDMA’s effects on serotonin and its empathogenic properties can help break down these barriers, allowing individuals to access and process emotions that are typically suppressed. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
4.1 MDMA and Emotional Processing
MDMA has been shown to facilitate emotional processing by allowing individuals to experience intense emotions in a safe and supportive environment. This can be particularly beneficial for people who have difficulty expressing emotions or who have repressed traumatic memories. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
4.2 The Therapeutic Alliance
The feelings of empathy and connection induced by MDMA can strengthen the therapeutic alliance between patients and therapists. This is critical for healing, as a strong therapeutic relationship can promote trust, safety, and vulnerability, all of which are essential for emotional healing. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
5. Risks and Considerations in MDMA-Assisted Therapy
While MDMA holds great promise as a therapeutic tool, it is not without risks. The drug’s potential to cause side effects and its history of recreational abuse raise important questions about its safety and efficacy in clinical settings. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
5.1 Side Effects and Potential Risks
Common side effects of MDMA include nausea, anxiety, increased heart rate, dehydration, and hyperthermia. These effects are typically short-term but can be dangerous if not properly managed. Additionally, MDMA use can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by excessive serotonin in the brain. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
5.2 Safety in Clinical Settings
To mitigate these risks, MDMA-assisted therapy is conducted in a controlled, clinical environment with medical supervision. Patients are carefully screened for any contraindications or underlying medical conditions that could increase their risk of adverse effects. Additionally, therapy sessions are closely monitored, and the dose of MDMA is carefully calibrated to ensure safety. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
5.3 Long-Term Effects
Although MDMA has been shown to be generally safe when used in clinical settings, there is still ongoing research into its long-term effects. Some studies have raised concerns about the potential for neurotoxicity and cognitive impairment with repeated use, particularly at high doses. Researchers need to conduct more studies to fully understand the long-term consequences of MDMA use, even in a therapeutic context. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
6. Conclusion: The Future of MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
MDMA’s potential as a therapeutic tool in mental health treatment is, without a doubt, an exciting area of research. Clinical trials have shown promising results in treating PTSD, anxiety, and depression, and the drug’s ability to enhance emotional processing and strengthen the therapeutic alliance makes it a unique tool in psychotherapy. However, as with any emerging treatment, risks and considerations require careful attention. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment
The continued study of MDMA in clinical settings will, therefore, help refine its therapeutic applications and, in turn, ensure that practitioners can use it safely and effectively. As researchers conduct more studies and the regulatory landscape evolves, MDMA-assisted psychotherapy may, consequently, become a viable treatment option for individuals with various mental health conditions. MDMA in Mental Health Treatment